

Inability to remember new acquaintances made after amnesia set in.
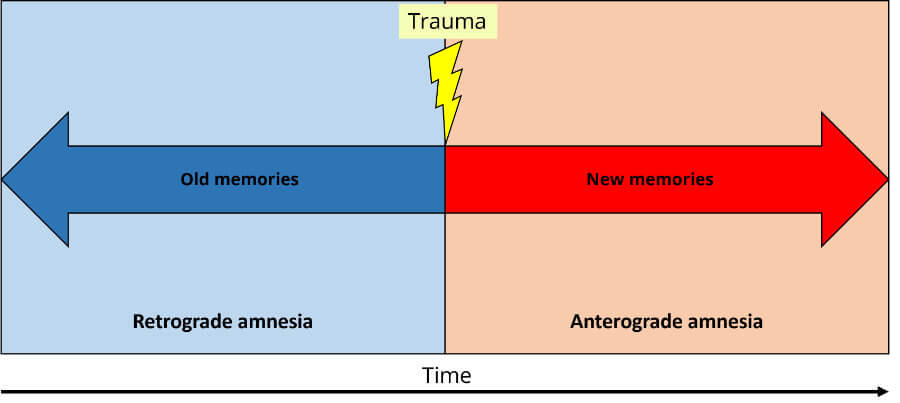
Trouble remembering life events that happened after the amnesia-causing event, like a move or job change.Other areas near the hippocampus can also be damaged, says Hascalovici, including the basal forebrain, fornix, and medial temporal lobe.Īccording to Hascalovici, these are some of the most common symptoms associated with anterograde amnesia: The hippocampus is a part of the brain located in the inner temporal lobe, which plays a key role in the long-term storage of new memories. Here's what to know about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for anterograde amnesia.Īs with other forms of amnesia, anterograde amnesia often happens when the hippocampus is damaged, says Hascalovici. Note: A small 2015 study showed that it's not uncommon for patients with anterograde amnesia to also have retrograde amnesia. "Occupational therapists and other professionals can help people with anterograde amnesia relearn certain skills and master tasks that support everyday functioning, like being able to go to appointments and schedule reminders of certain daily commitments," he says.
#Anterograde amnesia vs retrograde amnesia journal articles full#
He adds that not all people with anterograde amnesia will experience a full recovery, but it's definitely treatable and sometimes temporary. Retrograde amnesia: Impairs your ability to remember anything that occurred before the amnesia set in but doesn't impair your ability to make new memories.Īnterograde amnesia is significantly more common than retrograde amnesia, according to Jacob Hascalovici MD, a board-certified neurologist and chief medical officer at Clearing.

As a result, you may have trouble recalling things that happened in the recent past - like what you had for breakfast - but easily remember things that happened prior to the amnesia-causing event.Ģ. Anterograde amnesia: Your brain becomes unable to form new memories or store new information after the amnesia-causing event. There are two main types of amnesia, or memory loss:ġ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
